6 Min Read
The consequences of poor quality control and quality inspection are not challenging to find. For example, searching up ‘product recalls’ on any search engine produces many results of raw materials, manufactured products, and intermediate goods having to be recalled because of poor product quality.
To prevent costly recalls and a loss of confidence in your business by customers, it is necessary to have a robust quality inspection process. A strong quality inspection process ensures that quality inspections are carried out promptly by a team of quality inspectors. This way, your business will have consistent quality assurance for the products you manufacture and receive from other companies.
On top of protecting business reputation, a robust quality inspection and quality management system is needed to eliminate errors during production, reduce future costs, and for achieving continuous improvement in the products offered to customers (this, in turn, will boost overall customer satisfaction and profits).
As a high amount of quality data is needed to improve the quality of products sold to customers, the contemporary quality inspection and quality control process is underpinned by sophisticated quality inspection software. Essentially, quality inspection software is part of a package of software solutions that help with the quality inspection process.
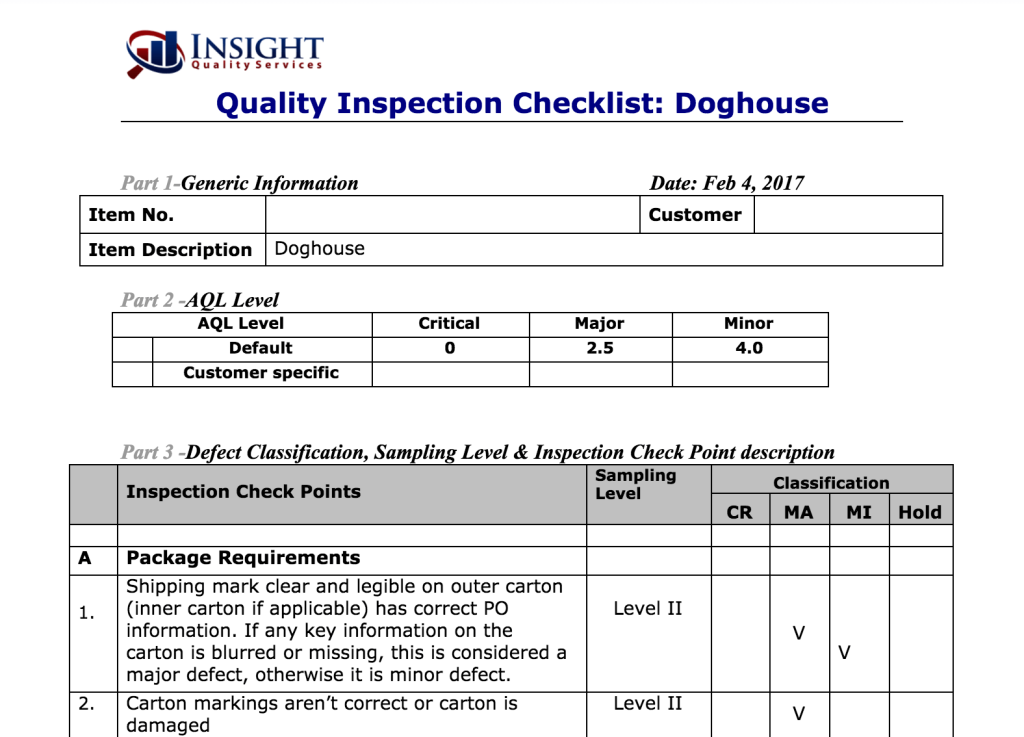
Although the importance of software solutions will be discussed in depth later, something that this software helps with immensely is sharing important documents between quality control inspectors quickly. This includes, among other things, the all-important ‘pre-established checklist,’ which contains the standards and specifications of products (these include raw materials, manufactured goods, finished goods, semi-finished goods, and other components) that manufacturers are expected to replicate.
Now, let’s discuss the nature of quality inspection in more depth and why your organization must prioritize it!
What is a Quality inspection?
As alluded to earlier, quality inspection is the act of performing an inspection on products to determine their overall quality. During these quality inspections, raw materials or manufactured goods are judged against a set of predetermined quality standards/dimensions and inspection criteria in order to assess the overall quality of a product. Thus, a quality inspection includes measuring unit dimensions, testing, examining, gauging, and observing overall product quality to locate any quality issues. As mentioned, these results are then compared to preformulated standards that determine the quality expectations of products.
Thus, a quality inspection has two broad purposes: to ensure that damaged or defective products are not sold/sent to customers, and that inspected products conform to predetermined standards and the specified requirements of clients/customers.
Responsibilities of a Quality Inspector
As well as inspecting products at various stages of the production process, quality control inspectors have additional responsibilities that are critical for guaranteeing a consistent production of quality products.
For a start, quality inspectors are expected to communicate the devised rules and standards to relevant staff at the organization. Additionally, quality control inspectors must also circulate documents to employees and production workers that outline the specified requirements for a particular product. Essentially, these specified requirements are created by external clients/customers and are sent to manufacturers. With both sets of documents circulated by inspectors, your company will have a good baseline established for quality inspection.
Of course, clients expect these relevant requirements to be followed during the entire production process. Thus, it is up to the inspectors to distribute these instructions to the development team and manufacturing team to ensure that products are manufactured according to these requirements and specifications.
Finally, quality control inspectors are responsible for circulating new standards and requirements to the relevant employees. As part of this responsibility, inspectors must ensure compliance with all existing regulations and standards that pertain to quality control.
Smarter Asset Tracking With NFC Tags
Learn more about how NonStop Suite's NFC Asset Tracking Solution can help your Enterprise streamline operations to new heights.
Get A Free Product Tour
Types of Quality Inspections
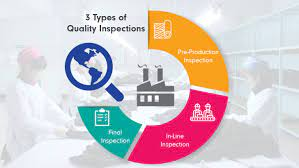
Different types of quality inspections take place during manufacturing processes. The type of quality inspection differs according to where the review takes place on the production line.
As a rule, detecting issues early in the manufacturing process is generally better. This is because early detection of errors enables organizations to intervene early; moreover, being able to reliably detect errors at an earlier stage is far less costly than detecting these issues later in the manufacturing process.
A helpful concept to remember here is the so-called ‘1:10:100 ratio.’ This ratio demonstrates the extent to which costs escalate the later a product fault is found in the manufacturing process and therefore underscores why inspecting earlier is better. Thus, should a product fault be found during the mass production phase, correcting the defect will cost 10x more than it would if the fault was discovered during the design stage. Likewise, fixing the error after the product has reached customers will cost 100x more following the logic of the ratio (finding a defect at this stage will also involve settling warranty claims).
This further underscores the importance of implementing and following quality control methods and measures at your company. Of course, there are several quality control measures and strategies that companies can decide to enforce. The different types of quality inspection that we will now discuss provide a good overview of how organizations can implement quality management procedures.
Raw Materials or Pre Production Inspection
A raw material or pre-production inspection occurs before the manufacturing process starts. When receiving materials from a new supplier or performing services for a large contract, these pre-production inspections become particularly important.
Of course, if the primary materials used for production are faulty, defective, or damaged, the final product will be affected, too. Moreover, the earlier these defects are detected, the less money a company will have to spend rectifying the issues, underscoring the importance of these pre-production inspections.
Manufacturing Process or During Production Inspection
An in-process inspection takes place after 15-20% of the total amount of products has been manufactured. As with other inspection checks at different stages, random samples are performed to determine if the manufactured products meet predetermined quality standards and the client’s specific requirements.
The in-process inspection is a vitally important stage in the quality inspection process. Essentially, the in-process inspection represents the last chance organizations have to detect defects before mass production. Thus, successful inspections at this stage are a ‘green light’ for organizations to continue manufacturing finished products.
Pre-Shipment Inspection
After 80% of production has been completed, the finished products are inspected prior to shipping. Inspectors will again assess products in a truly random manner to determine if they can be sent to clients/customers. This pre-shipment inspection is akin to a final inspection as it is the last opportunity to spot defects and take the appropriate corrective actions before the products are shipped. After the final inspection, products are packaged in preparation for shipping.
Loading and Unloading Inspection
Finally, these last inspections are essential for guaranteeing the safe transport of products. Thus, inspectors must first ensure that products have been packaged correctly to prevent damage during transportation. Moreover, the inspectors must verify product quantity, product information, and packaging compliance before the products are sent to customers.
Once this data has been verified, quality control inspectors must guarantee the quality of the containers that will ship the products. This process includes checking the container for leaks and that the container has sufficient ventilation (insufficient ventilation can result in dampness/mold developing on some raw materials, thereby leading to product spoilage).
How is Quality Inspection Different From Quality Control?
It is helpful to explain the differences between quality inspection and quality control. Although the two terms seem interchangeable, there are considerable and important differences between them.
Quality inspection is solely concerned with the post-production checks of products. In other words, quality inspection only ensures that defective units or faulty products do not leave the factory to clients. Importantly, these final inspections will not affect the production of goods as quality inspection is not concerned with the production process.
By contrast, quality control (QC) is directly concerned with producing goods. During the production process, quality inspectors and workers work together to improve product quality. For example, inspectors and manufacturing workers can distinguish good products from defective products based on quality inspection tests. Following this, workers and inspectors can work together to understand the causes of problems and improve the process. Thus, with quality control, organizations are concerned with achieving continuous improvement in the products offered to customers.
A different way to conceptualize the difference between quality inspection and quality control is to think of quality inspection as a component of quality control. While quality inspection is concerned with detecting issues as soon as possible in the manufacturing process, the focus of quality control is far broader.
Formulate a Checklist for a Smooth Quality Inspection Process
Earlier, we mentioned the importance of having a pre-established checklist to determine if the manufactured products meet standards and the client’s preferences.
Of course, determining if you are producing quality products is far easier if you have a checklist on-hand. As mentioned earlier, these checklists must be distributed by quality inspection managers to the manufacturing team. Without the guidance of these checklists, it will be challenging for a quality control inspector (even an experienced inspector) to determine if the products have been manufactured correctly. Moreover, critical processes will be delayed at the manufacturing plant without on-hand checklists because of an encumbered quality inspection process.
This underlines the need for a checklist when conducting any quality inspection. Moreover, with the assistance of an effective quality management solution, it is possible to further improve efficiency regarding sharing checklists and critical documents among employees.
Wrapping Up!

A quality inspection software solution can immensely help your organization with the quality inspection process. We have already mentioned that software solutions make paper documents redundant (as essential documents and criteria-based inspection plans are shared and saved on a cloud network).
Should your organization require assistance establishing a robust cloud-based EAM system or with work & process digitalization, you should consult with the NonStop Group. The NonStop Group has a wealth of experience helping clients in diverse industries establish sophisticated asset management systems and cloud networks. With assistance from the NonStop Group, your organization can see a reduced administrative workload and an improvement in the quality control process.
If you want these results for your company, make an appointment with the NonStop Group today!